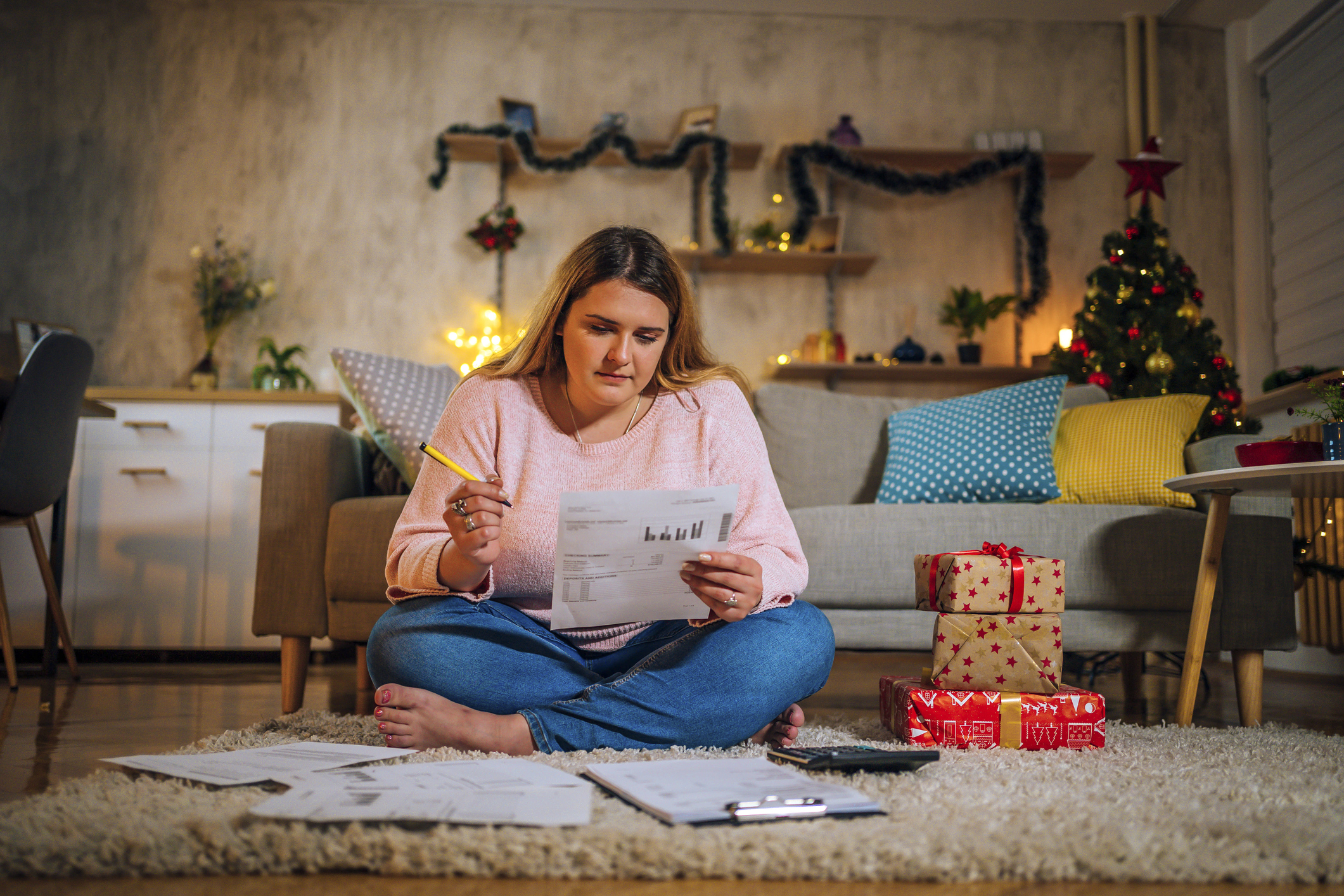
The chairman of the Federal Reserve held a press conference following the F.O.M.C. meeting. Watch his opening remarks in the video above.
WASHINGTON (AP) — The Federal Reserve said Wednesday that greater progress has been made in reducing inflation to its 2% target, a sign that the central bank is moving closer toward cutting its key interest rate for the first time in four years.
In a statement issued after it concluded its two-day meeting, the Fed also said that “job gains have moderated” and acknowledged that the unemployment rate has risen. The Fed is required by Congress to pursue stable prices and maximum employment, and the statement said the central bank is “attentive to the risks” to both goals, a shift after several years of focusing exclusively on combatting inflation.
Fed policymakers also chose to keep their key rate at a 23-year high of 5.3%, even as many Democratic elected officials and some economists have pushed for lower rates to bolster the economy and prevent job cuts. Republicans, including former President Donald Trump, have argued that a rate cut before the election would appear politically motivated.
Before the Fed’s decision, financial market traders had priced in 100% odds that the central bank will reduce its benchmark rate at its Sept. 17-18 meeting, according to futures markets. The Fed typically seeks to avoid surprising investors with its rate decisions.
Still, the Fed repeated in its statement that “it does not expect it will be appropriate” to reduce borrowing costs “until it has gained greater confidence” that inflation is steadily falling to 2%, which clouds the timing of a rate cut.
THIS IS A BREAKING NEWS UPDATE. AP’s earlier story follows below
With the end of their two-year fight against inflation in sight, Federal Reserve officials are likely Wednesday to set the stage for the first cut to their key interest rate in four years, a major shift in policy that could eventually lower borrowing costs for U.S. consumers and businesses.
Inflation has been falling steadily closer to the Fed’s 2% target for the past several months. And the job market has cooled, with the unemployment rate rising about a half-point this year to 4.1%. Fed officials have said that they are seeking to balance the need to keep rates high enough to control inflation without keeping them too high for too long and causing a recession.
Rate cuts — as early as September — could help the Fed achieve a “soft landing,” in which high inflation is defeated without an economic downturn. Such an outcome might also affect this year’s presidential race, as Republicans have sought to tie Vice President Kamala Harris to the inflation spike of the past three years. Former President Donald Trump said the Fed shouldn’t cut rates before the election.
“While I don’t believe we have reached our final destination, I do believe we are getting closer to the time when a cut in the policy rate is warranted,” Christopher Waller, a member of the Fed’s governing board, said earlier this month.
Financial market traders have priced in 100% odds that the central bank will reduce its benchmark rate at its Sept. 17-18 meeting, according to futures markets, so Fed Chair Jerome Powell does not need to provide further guidance to markets Wednesday about the timing of a cut, economists say.
Instead, Powell will have more opportunities in the coming months to illustrate how the Fed is thinking about inflation and interest rates, particularly in his speech in late August at the annual Fed conference in Jackson Hole, Wyoming. As a result, he may not provide much of a hint Wednesday regarding how quickly the Fed will cut rates after it starts doing so. Economists expect relatively gradual cuts, unless there is evidence the job market is faltering, which would spur the Fed to move faster.
Even so, the Fed could alter several parts of the statement it releases after each meeting to lay the groundwork for a cut in September.
In the statement it released after its June meeting, for example, Fed officials said, “In recent months, there has been modest further progress toward the (Fed’s) 2% inflation objective.” On Wednesday, the Fed could drop “modest” or alter it in some other way to underscore that additional progress on inflation has been achieved.
In the latest piece of good news on price increases, on Friday the government said that yearly inflation fell to 2.5% in July, according to the Fed’s preferred inflation measure. That is down from 2.6% the previous month and the lowest since February 2021, when inflation was just starting to accelerate.
One encouraging sign for the Fed is that rental prices, a key driver of broader inflation, have started to noticeably cool, as new apartment buildings have been completed in many large cities.
Rental inflation was a leading example of what economists call “catch-up” inflation, in which prices were still rising this year because of distortions from the pandemic economy. Many Americans sought more living space or moved out on their own during COVID, pushing up the cost of rents and homes.
The government’s rental inflation measures have been rising faster than usual, well into this year, to reflect those increases. This even as rapid apartment building has slowed cost increases for new leases. Other examples of “catch-up” inflation include car insurance, which soared more than 20% earlier this year from a year ago, as insurance companies have charged more to reflect the pandemic-era spike in new-car prices. Yet, even car insurance costs have started to rise more slowly.
Powell has long said the Fed was seeking “greater confidence” that inflation was falling back to the Fed’s 2% target. Earlier this month — even before the latest inflation readings — he said that recent inflation data does “ add somewhat to confidence ” that it is cooling.
Powell and other Fed officials have also worried that strong job growth and rapidly rising paychecks would potentially fuel inflation, as some companies would likely raise prices to offset the higher labor costs.
But hiring and wage growth have slowed in recent months, and Powell this month acknowledged the job market is “not a source of broad inflationary pressures for the economy.”
On Wednesday, the government released a quarterly measure of wage growth, which showed that paychecks, while still growing at a healthy pace, are not growing as fast as three months ago, adding to evidence that inflationary pressures have eased.